It is almost impossible to do without paper in everyday life. This will not happen for many centuries. What did they make of it before, and what are the production technologies today?
How and from what did paper make before?

How much humanity remembers itself, it writes its own story. First, in the form of cave paintings, clearly telling about the life of ancient tribes. Later in Egypt, writing sheets were prepared from stems of papyrus. The Romans used plaques covered with wax. And in India preserved dried tiles of elephant droppings with ornate inscriptions.
The Chinese are considered to be the creators of the paper prototype (around 105 AD). Initially, it was made from the waste of mulberry cocoons by grinding, thorough drying and pressing. But such a manufacture was expensive and time-consuming. Then the attention of craftsmen was attracted by hemp nettle. However, the sheets that were obtained from it, in finished form, remained too coarse.

The best raw material was the bark of a mulberry (mulberry) tree. Its fibers, mixed with hemp, ash and water, were crushed by hand, boiled and laid on a bamboo sieve. After prolonged drying in the sun, they were leveled with stones. Strong and thin sheets turned out. Adhesives, starch and dyes were added for improvement. For a long time, the intricacies of this man-made work were kept secret. According to some sources, persistent Arabs managed to find out the secrets of the masters under torture.So the paper migrated to Asia, and from there to Europe. Enterprising Germans were quick to open the first factory in the 13th century.
Modern production
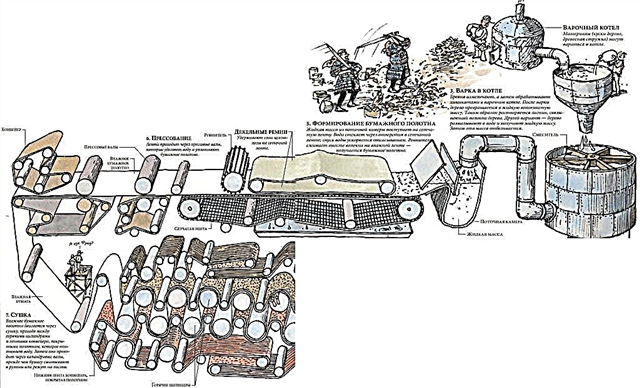
Previously, paper was made from cotton, silk and linen rags. Today, the main material is wood.. Softwood, birch, poplar, chestnut, eucalyptus are leading. Large enterprises are famous for Canada, Russia, the USA, Scandinavia, Japan, Germany. Combines are fully automated.
Logs are delivered to the workshop, where the aggregates clean them of bark. The resulting material is ground to fine fibers (fibrils). Mix with water for swelling, and again remove the residual chips. Then a homogeneous mass is placed in special boilers, where it is cooked in a mixture of potent acids. In the same way, bark and wood chips are separately treated, converting to cellulose.
Then it is mixed with fiber fibers, waste paper (ink previously removed) and continue to process in an acid brew. To give opacity to future paper, kaolin is added. Glue admixtures contribute to the smoothness of the surface and water-repellent properties. Various oxides are used in the production of special grades of expensive paper web.

It is the turn of the main mechanical giant of the mill - the paper machine. The giant reaches a length of 100 m, a width of 18-20 m. Between its two shafts a metal mesh is constantly rolling. On its surface is laid raw materials that have gone through several stages of processing.Unnecessary moisture flows through the cells, and the mass is evenly distributed on the surface.
Further, the material enters under the huge press shafts to form the web. After them, the drum-irons iron the giant sheet, removing the remaining water. And at the end, huge calendars press the paper surface, giving it a finished look. Now you can send rolls for cutting and packing in sheets of different sizes.
Human needs for paper do not dry out, and its production is considered harmful. Damage is afflicted to forests that are being massively felled. Combines use acids. Waste, harmful substances enter water bodies nearby, into the air. From 1 ton of paper, you can make 30,000 school notebooks. But to get it, you have to cut down 17 trees. It is important to replenish natural resources. Then, after centuries, you don’t have to take children to museums to explain what paper is and how important it used to be.